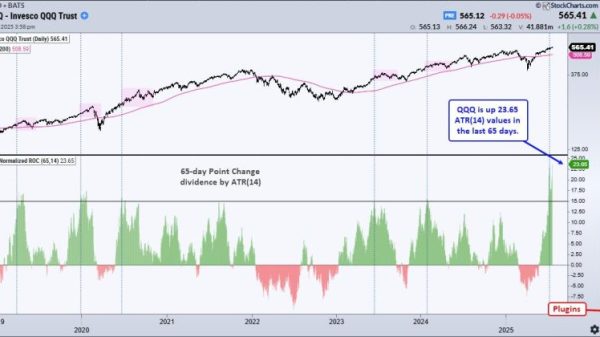
The world’s mining industry may be spread across more than 150 countries, but new data reveals that almost half of all large-scale mining and processing facilities are concentrated in just three: China, Australia, and the United States.
The International Council on Mining and Metals (ICMM) on Wednesday (September 3) released its Global Mining Dataset report, a sweeping compilation of 15,188 mines and processing plants that it says is the most comprehensive public record of the sector to date.
According to ICMM, 45 percent of all mines, smelters, refineries, and steel plants are clustered in China, the US, and Australia: an uneven distribution that has significant implications for supply chains and the pace of the clean energy transition.
“ICMM’s foundational Dataset shows that over 75 percent of national economies have at least some connection to large-scale mining or mineral processing,” said Rohitesh Dhawan, ICMM’s president and CEO.
“Having a global view of the location, type, commodity and footprint of these facilities is essential to inform the right public and policy debates for this critical sector. With minerals and metals at the heart of the energy transition and geopolitical shifts, robust, global, industry-wide data has never been more critical.”
The dataset identifies 12,876 mines, 1,980 standalone processing facilities, and 332 co-located sites where extraction and processing happen together.
While operations stretch across more than 151 countries, ICMM’s analysis shows that China in particular dominates the processing stage of the supply chain. The dataset records 426 metallurgical facilities in China — by far the largest number worldwide — compared with 120 in the US, 87 in India, and 65 in Brazil.
That asymmetry between mining and refining presents a challenge facing local supply chains. While resource deposits are scattered globally, the industrial capacity to convert ores into usable metals is more centralized and heavily tilted toward China.
Europe, for instance, suffers from this vulnerability. Despite having strong demand from its automotive, aerospace, and electronics industries, the continent’s mining base has shrunk. The dataset shows a greater density of metallurgical facilities in Europe compared with mines.
This imbalance is not limited to Europe. Across the globe, many economies have significant mineral deposits but lack the facilities to process them. This structural gap cements the dominance of China which has invested heavily in refining capacity and controls much of the midstream in critical mineral supply chains.
Coal remains dominant
Although the dataset highlights the role of critical minerals in the energy transition, it also shows that coal remains the single most common mined commodity by number of facilities.
Coal accounts for 42 percent of all mines, followed by gold at 17 percent, copper at 12 percent, and iron ore at 9 percent.
The prevalence of coal mines contrasts with global climate goals, but also reflects the legacy infrastructure of energy systems and the uneven pace of transition.
Overall, Asia hosts the largest number of coal, copper, and iron ore mines, while North and Central America contain the highest number of gold mines.
Playing the long game
ICMM officials stressed that the release of the dataset is just a first step in a multi-year effort to improve transparency and support evidence-based policymaking in the sector. Alongside the full dataset, which draws on proprietary sources, ICMM published a public version covering 8,508 facilities.
Dhawan said the council hopes the data will “continue to expand and improve through partnerships” while building on key sustainability indicators in the coming months.
More crucially, industry observers have long criticized the scarcity of comprehensive, public data on the sector. Without standardized information, they argue, it is difficult to evaluate the social and environmental impacts of mining or even craft effective regulations.
ICMM’s initiative, though still limited by licensing restrictions on some proprietary datasets, represents one of the most ambitious attempts to date to assemble a global picture of the industry. The council said it would work with partners to expand the dataset and incorporate indicators on sustainability performance.
Securities Disclosure: I, Giann Liguid, hold no direct investment interest in any company mentioned in this article.